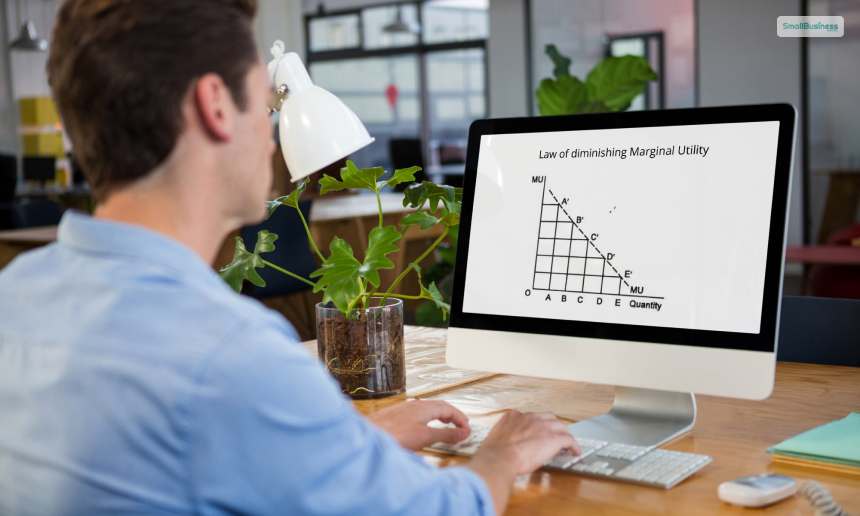
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that as one consumes additional units of a particular good, the amount of satisfaction coming from the product decreases.
Basically, as you consume more of a particular type of good, you will feel that the satisfaction with that good is decreasing with time. Marginal utility is a change in the level of utility of a good that comes with the consumption of another unit of that same good.
In this article, you will learn about the law of diminishing marginal utility and how it generally works. Apart from that, you will also learn about the application of this law in the context of business.
Finally, we will also explain why this law impacts prices in business, along with some simple examples. Hence, to learn more about diminishing marginal utility, read through to the end of the article.
What Is The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility?
According to Investopedia,
“The law of diminishing marginal utility states that all else equal, as consumption increases, the marginal utility derived from each additional unit declines. Marginal utility is the incremental increase in utility that results from the consumption of one additional unit. “Utility” is an economic term used to represent satisfaction or happiness.”
It is an economic principle or an economic term to denote the marginal utility of a good or service. As per this law, the marginal utility decreases with the increment of its quantity in consumption. It suggests that the satisfaction or the utility derived from a product or a service goes down with it going into more use.
Simply put, this law states that if you consume more of a particular item, the level of satisfaction that comes from that same item decreases. The more you consume, the lesser the satisfaction gets. The satisfaction of that product is shown as utility for this law.
In microeconomic models, the demand curves for this law are downward sloping. This is because, here, as you add more goods and services, their usage and value will decrease with time. Before its application, the law assumes rational consumers, standard size of units, and continuous consumption.
There are exceptions to diminishing marginal utility too. Some of them are addictions, hobbies, unrealistic assumptions, rare items, and more.
How Does The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility Work?
Wall Street Mojo gives a simple example –
“Suppose a person is starving and has not eaten food all day. When he finally starts to eat, the first bite will give him a lot of satisfaction. As he keeps eating more and more food, his appetite will decrease and come to a point where he does not want to eat anymore.”
If we explain this in simple words, the law of diminishing marginal utility is similar to reducing your craving for food when you start to eat. The first bites of the food you eat when you are hungry is always the most satisfactory.
But, if you keep eating more, your hunger goes down so does the satisfaction. You can take your favorite food for example, and you’ll see that the last slice of pizza doesn’t seem as enjoyable as the first one was.
However, this gets more complicated with the increasing complexity of the situation. In a business situation, as a customer consumes more of a product, the satisfaction from the product that the customer derives decreases. This means that the more a person uses a particular product, the more the product loses its value.
This can also happen due to changing interests of the product or the reduction in the need for the product. In another situation as well, this concept occurs if the customer feels more familiar with the product.
The effect on the product also decreases the likelihood that the customer does a repurchase. This, in turn, decreases the demand for the product. This is the major reason why economists record the demand for the product in downward slopes in microeconomic models.
How Does Diminishing Marginal Utility Work In Business?
According to Indeed.com,
“The law of diminishing marginal utility concerns many aspects of a company’s operations. For example, marketing professionals often aim to adjust the number of items in stock and improve sales strategies using this law. It helps in making a marketing strategy that balances the marginal utility of different products. It allows them to maintain customer base satisfaction while targeting new customers.”
This applies to business as well. The law of diminishing marginal utility can affect profitability and how much customers need a product or service, making its need reduce with time.
In business, the law suggests that the customers will start to get less value from buying more of what a business is selling. This factor influences the pricing strategies and product diversification, and the marketing tactics for encouraging customers to try new offerings instead of buying more of the same service or product.
In business, analysts consider marginal utility as the enjoyment that the consumer gets with each additional consumption of the product. Here, the business calculates the utility of the product beyond the consumption of the first product. If a consumer buys a water bottle and buys a second one later, the utility or satisfaction that the customer gains is marginal utility.
However, the law of diminishing marginal utility is directly related to the diminishing price of the product. As the satisfaction from a product or its utility decreases with the increase in its consumption, consumers do not like to pay the same for the product. Rather, they like to pay less.
This law basically dictates how a company operates with its products and services. A company might adjust how many goods it has in its inventory and also its sales tactics once it considers the application of the law. Apart from that, the marketing strategy of a company also considers balancing the marginal utility across product lines.
Does The Law Affect Pricing In Business?
How a business prices its goods and services depends a lot on the law of diminishing marginal utility. Since a good has more utility in its first time, consumers are willing to pay more to try a new product.
For example, a company sets the price of a bag as $30. However, for a set of two, its price is $55, and the cost for a set of three is $75. A customer looking for bags can get the best price if they buy three.
However, not every customer will need three bags, even though they constitute the best deal. Anyone who is shopping for a bag might need only one at the moment. Hence, the price of the first bag is the highest, as per the given situation. After that, the bag’s marginal utility decreases. Hence, the business decreases its cost per unit in order. With the help of it, the business entices its shoppers to purchase more.
How can Small Businesses Apply the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility?
Small businesses can take advantage of this principle to understand customer behavior and what’s impacting their sales and improve their pricing strategy. Following are some examples to help you understand –
Cafe
If you are a cafe and bakery owner, you can start to add extra value to the customers by offering a combo meal. Here, you’ll offer your customers a pastry with a cup of coffee at a discounted price. This will help you grow your customers and get more clients your way.
Small Boutiques
If you are a clothing store owner, you can arrange for additional discounts for frequent customers. This will help you increase customer loyalty and help sustain cash flow. Also, you can diversify the types of outfits your business provides.
Local Bakery
your customers might get tired of the bakes even if they are a local favorite. You can break the monotony and bring back the customers who are losing interest by offering something new. Sometimes, special pastries or adding seasonal flavors to the cake-shelf can help you innovate.
Wrapping Up
According to the law of diminishing marginal utility, the marginal utility decreases the more you increase your consumption of the item. With time, the marginal utility becomes a negative utility, with more consumption of the given product. Hence, it might become fully unfavorable for people to consume another unit of the same product.
The law of diminishing marginal utility is very useful for marketers as the latter wants to ensure that the marginal utility for any product remains high as they sell the product. Do you have anything more to add regarding this law? Share your thoughts and opinions with us in the comments section below.
Continue Reading:



Leave A Comment